1. What is a steering system in automotives?
The steering system is one of the most important systems in a vehicle, with a complex structure composed of various components and mechanisms that support each other in performing distinct functions. The steering system is used to change the direction of the vehicle, ensuring the rotation axis of the wheels follows the correct kinematic principles to reduce tire wear during turns and maintain the vehicle's motion in a desired direction, such as turning left, turning right, or going straight.
 The steering system helps the vehicle follow a defined path (Source: internet)
The steering system helps the vehicle follow a defined path (Source: internet)
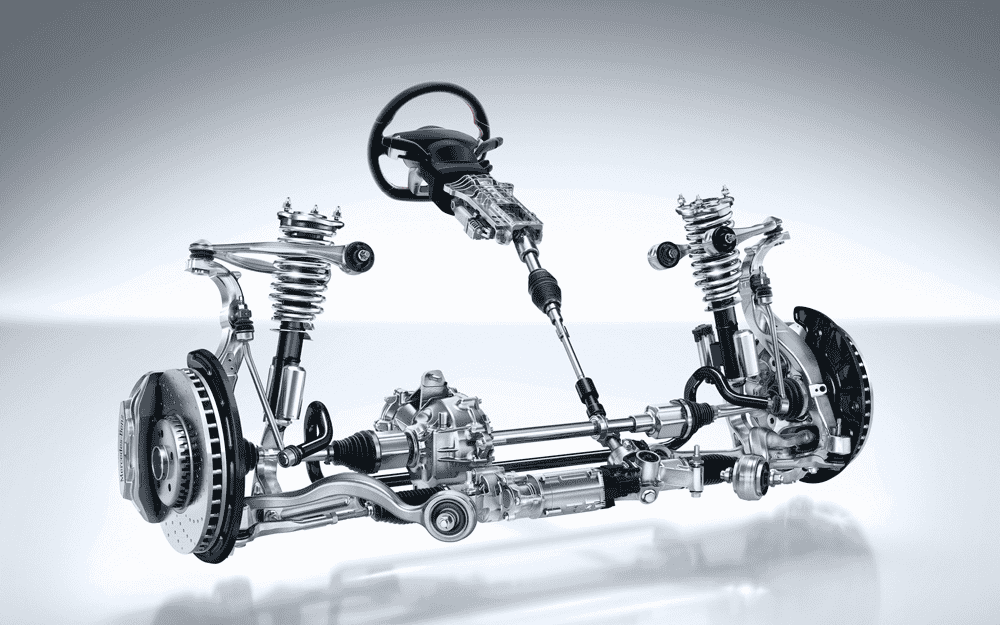
2. Structure of the automotives steering system
 General structure of the automotives steering system (Source: internet)
General structure of the automotives steering system (Source: internet)
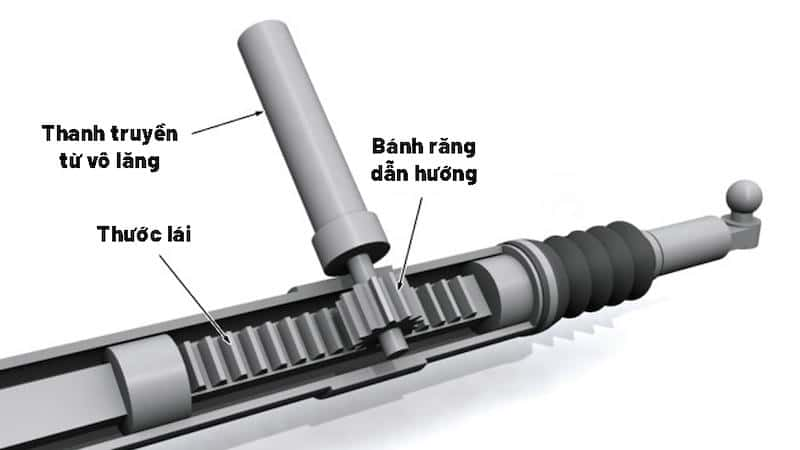
2.1. Steering mechanism
This component transmits the driver’s movements to the steering mechanism, allowing the wheels to rotate in the desired direction. Additionally, it receives feedback from the road, enhances the driving experience, and ensures driver safety in case of collision. The steering mechanism includes the following parts:
- Steering wheel: A component used by the driver to control the direction of the vehicle, integrating several other features to assist the driving process.
- Steering shaft: A metal tube connected to the steering wheel and steering mechanism, responsible for transmitting the torque from the steering wheel to the steering mechanism.
- Steering link: A component that links the steering mechanism and the steering mechanism drive, with joints that allow the link to rotate at different angles.
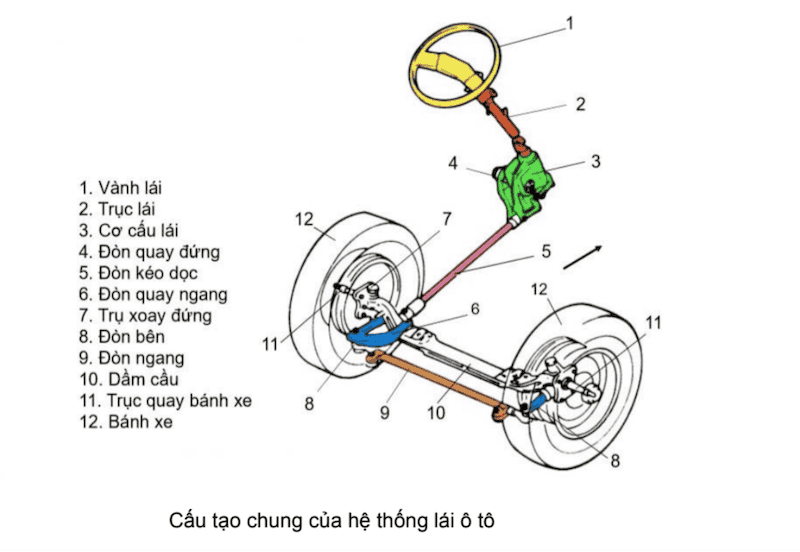
2.2. Steering mechanism
The steering mechanism controls the lever arms within the steering kinematic system, ensuring the wheels rotate according to the Ackerman principle. There are two common types of steering mechanisms:
- Rack and pinion steering: This simple structure is suitable for SUVs, small trucks, or passenger cars.
- Recirculating ball steering mechanism: This more complex system is suitable for large trucks or buses.
-
 Recirculating ball steering mechanism (Source: internet)
Recirculating ball steering mechanism (Source: internet)
2.3. Power steering
Power steering assists in reducing the effort required to turn the steering wheel when necessary, using an external energy source such as electricity, hydraulics, or pneumatics. This system is complex and often improved with various types of power steering, two of the most common being:
- Hydraulic power steering: This type generates high oil pressure to push a piston in the steering mechanism, rotating the gears or screw to assist with steering.
- Electric power steering: This type uses an electric motor to generate torque, rotating gears or screws to assist in steering.
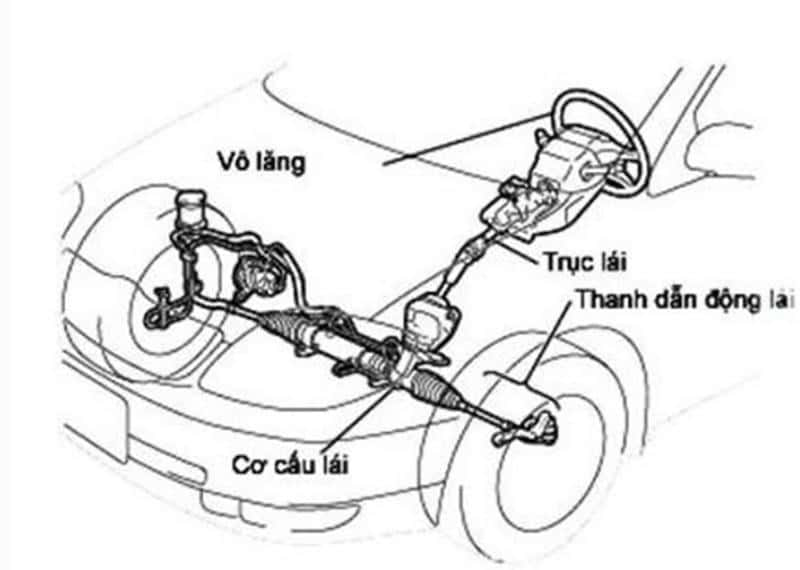 Structure of the steering system in an automotives (Source: internet)
Structure of the steering system in an automotives (Source: internet)
3. Operation principle of the automotives steering system
The operation principle of the steering system is complex, consisting of several basic principles depending on the active position.
3.1. Operating principle of the hydraulic power steering system
A hydraulic power steering system uses a hydraulic pump to create high oil pressure, pushing a piston in the steering mechanism to rotate gears or screws. The operating principle is as follows:
- When the driver turns the steering wheel, the steering shaft rotates and activates the hydraulic pump, generating high oil pressure.
- This pressure is transferred to a control valve, which distributes the oil pressure to two different lines, depending on the direction of the steering wheel.
- These lines connect to both sides of a piston in the steering mechanism. As high-pressure oil pushes the piston, it rotates the gears or screws within the steering mechanism.
- The gears or screws move the rack, causing the steering link to move vertically, which in turn moves the wheel link, causing the wheels to rotate at the desired angle. The wheels rotate according to the Ackerman principle, where the inner wheels turn at a larger angle than the outer wheels to minimize friction and improve vehicle stability when turning.
 Hydraulic power steering system (Source: internet)
Hydraulic power steering system (Source: internet)
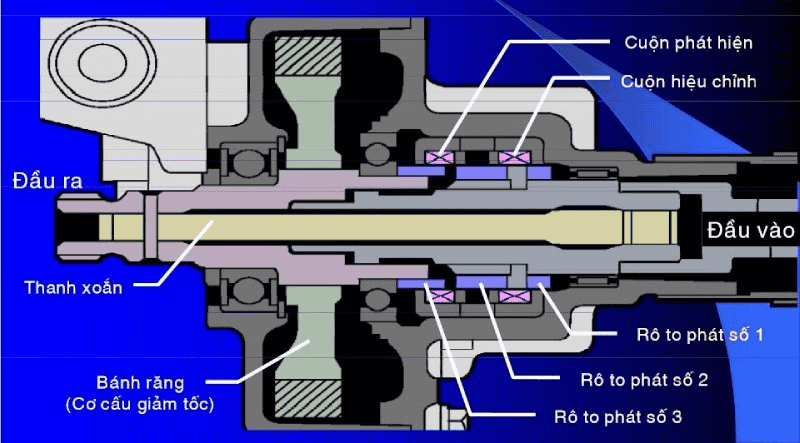
3.2. Operating principle of the electric power steering system
An electric power steering system uses an electric motor to generate torque, rotating gears or screws to assist in steering. The operating principle is as follows:
- When the driver turns the steering wheel, an angle sensor detects the movement and sends an electronic signal to a microprocessor, which controls the electric motor. The microprocessor calculates the necessary level and direction of the motor's rotation based on the steering angle.
- The electric motor rotates a gear or screw, which turns the steering mechanism gears or screws.
- These gears or screws move the rack, causing the steering link to move vertically, which in turn moves the wheel links, causing the wheels to rotate at the desired angle. The wheels rotate according to the Ackerman principle, with the inner wheels turning at a larger angle than the outer wheels, minimizing friction and improving vehicle stability when turning.
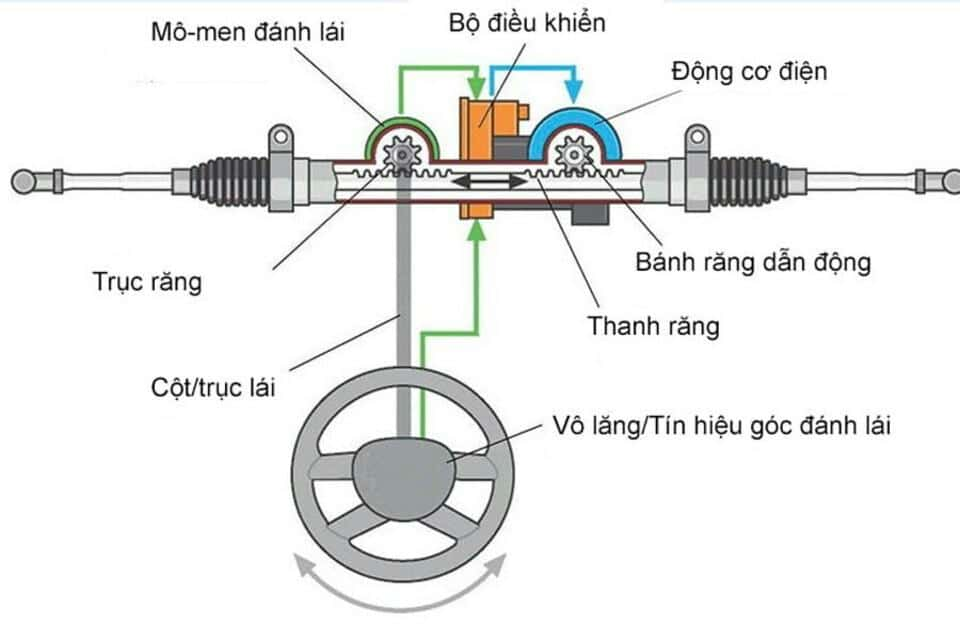 Electric power steering system (Source: internet)
Electric power steering system (Source: internet)
4. Types of automotives steering systemm
To meet the evolving demands of the automotives industry and users, steering systems are constantly being improved and developed. Currently, there are six types of steering systems, each with its own unique features.
4.1. Pure mechanical steering system
This system, developed in the mid-20th century, is no longer used in modern vehicle production. The system consists of two components: the steering drive, which transmits motion from the steering mechanism to the wheels, and the steering mechanism, which converts torque between the large turning angles of the wheel and the turning radius of the steering wheels.
4.2. Hydraulic power steering (HPS)
Developed to save energy when turning the vehicle and prevent shock from the wheels on the steering wheel, the HPS system is a development of the pure mechanical system. In Vietnam, this system is popular due to its low cost and suitability for urban driving speeds.
The system uses oil pressure to assist in changing the direction of the wheels. It is a closed-loop system using pressurized hydraulic fluid to change the front wheel angles based on the steering angle, making the steering easier for the driver.
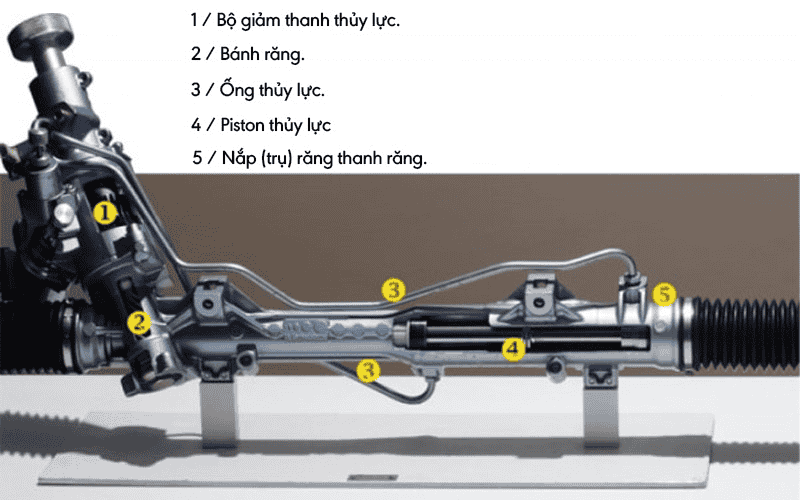 The hydraulic power steering system (HPS) includes Hydraulic dampers, gears, hydraulic hoses, hydraulic pistons, and rack gear covers (Source: internet)
The hydraulic power steering system (HPS) includes Hydraulic dampers, gears, hydraulic hoses, hydraulic pistons, and rack gear covers (Source: internet)
Advantages of hydraulic power steering:
- Simple structure, fewer parts, easy to repair and maintain
- Stability: The hydraulic power steering system quickly returns the steering wheel to the center, making steering adjustments easier
- High safety during operation
Realistic driving feel: The mechanical and hydraulic structure provides authentic road feedback, allowing the driver to feel road forces on the steering wheel
4.3. Electronically Controlled Hydraulic Power Steering (EHPS)
Due to its wide speed range, this system is commonly found in luxury and mid-range vehicles in Vietnam.
The system consists of a steering mechanism, steering drive, and an electronic control unit (MCU) that directly controls the power steering valve instead of the torsion bar.
Advantages of EHPS:
- Fuel-saving (about 2.8% compared to conventional hydraulic power steering)
- Motor speed control
- Lower noise
- Power assistance adjusts based on steering conditions
4.4. Electric Power Steering (EPS)
The EPS system replaces the oil pump with an electric motor, a significant difference from traditional systems. In vehicles with this system, power assistance is based on road resistance.
Specifically, torque sensors on the torsion bar detect road resistance acting on the system. Combined with other sensors and vehicle condition data, the system adjusts the assistance ratio by controlling the electric motor directly.
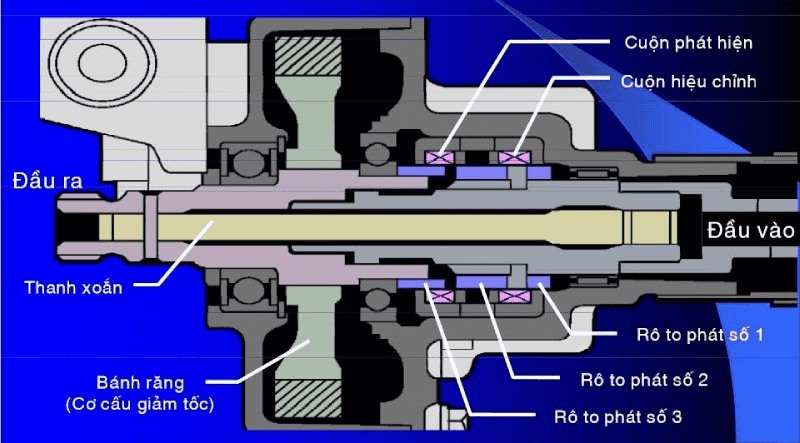 Torque sensors on the torsion bar detect road resistance, adjusting the assistance ratio through direct control of the motor (Source: internet)
Torque sensors on the torsion bar detect road resistance, adjusting the assistance ratio through direct control of the motor (Source: internet)
Advantages of EPS:
- Energy-saving and improved fuel efficiency
- Light and easy driving experience
- Enhanced control and stability
- EPS can integrate with other technologies and systems in the vehicle
4.5. Active Steering System (AFS)
The AFS is an electronically controlled electric power steering system found in high-end vehicles, often combined with power assistance to create a complete steering system. AFS uses sensors to gather input data from the vehicle's ECU, generating force (either assistance or resistance) in the electric motor. This system analyzes the vehicle's motion at different speeds and conditions, making decisions based on steering angle and vehicle body rotation.
The steering assistance is fixed on the steering column (EPAS-column), steering rack (EPAS-rack), or added to a reducer mounted on the steering rack (EPAS-pinion), parallel to the steering rack (EPAS-dual-pinion). The steering direction at low speeds is primarily determined by the steering angle.
Advantages of AFS:
- Light and easy driving experience
- Space-efficient
- Low engine power consumption
4.6. Steer-by-wire system
The Steer-by-wire system uses an ECU to control the hydraulic flow to the steering rack, along with an angle sensor. The system also includes a clutch to directly connect the steering wheel to the rack in emergency situations.
Additionally, the system includes a camera to monitor movement and directly adjust the steering rack to change the wheel direction.
There are two types of Steer-by-wire systems:
- Independent Steer-by-wire: Each wheel has its own controlling motor
- Integrated Steer-by-wire: The two front wheels are connected through the steering kinematic system