The scientific research topic on "Principles of ABS Pump Operation" holds significant importance in the field of automotive safety technology, particularly in the context of increasing emphasis on traffic safety and stability. The Anti-lock Braking System (ABS) is a pivotal innovation that enhances vehicle control and safety during sudden braking. The ABS pump plays a crucial role in maintaining optimal brake pressure, preventing wheel lock-up, and thereby reducing the risk of skidding and loss of steering control.
This study delves into the principles underlying the operation of the ABS pump, encompassing its structure, functions, operational mechanisms, and recommendations for inspection and maintenance methods. Furthermore, the research explores recent technological advancements aimed at improving the performance and reliability of ABS systems. This study not only provides foundational knowledge but also opens new pathways for the design and application of advanced braking systems, contributing to improved road safety and user experience.
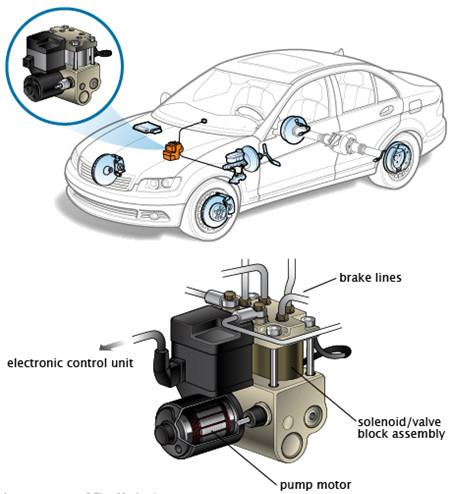
Figure 1: ABS Hydraulic Pump Assembly. (Source: Internet)
Functions and Roles of the ABS Pump
Functions of the ABS Pump
- Brake Pressure Regulation: The ability to adjust brake pressure for individual wheels prevents lock-up during sudden braking, maintaining driver control and vehicle stability.
- Rapid Feedback: The pump quickly responds to changes in road conditions and wheel speeds, adjusting brake pressure in real time to optimize braking efficiency.
- Emergency Braking: Optimizes braking force to minimize stopping distance and time while preventing wheel lock-up and loss of vehicle control.
- Integration with Other Systems: The pump is typically integrated with other safety systems such as the Electronic Stability Program (ESP) and Electronic Brakeforce Distribution (EBD).
Roles of the ABS Pump
- Enhanced Safety: It enables drivers to maintain vehicle control even during emergency braking scenarios.
- Improved Handling: Drivers can navigate more effectively during sudden braking or on adverse road conditions (wet, icy, etc.), reducing skidding and maintaining the desired direction of travel.
- Reduced Tire Wear: By preventing wheel lock-up and skidding, the pump minimizes tire wear and extends tire lifespan.
- Support for Other Safety Systems: The ABS pump operates as a component of the vehicle's overall safety system, ensuring the effective performance of complementary systems like ESP and EBD, thereby providing a safer and more reliable driving environment.
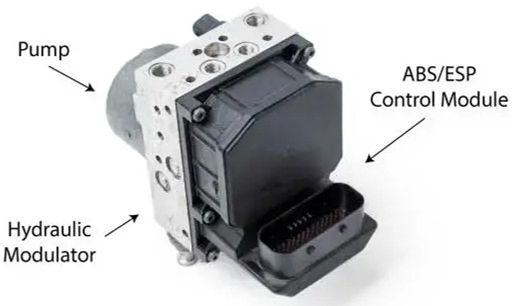
Figure 2: Overview of ABS Pump Assembly. (Source: Internet)
The ABS pump assembly typically consists of the ABS/ESP Control Module, an electric motor, solenoid valves operated by electromagnetic coils, and a base connecting the brake fluid lines (from the master cylinder to the wheel brake cylinders). The ABS control module acts as a computer, receiving signals from wheel speed sensors and other sensors, such as brake pedal switches, steering angle sensors, and acceleration sensors. Based on these inputs, the ABS ECU calculates the optimal brake pressure for each wheel and commands the pump to adjust the pressure accordingly.
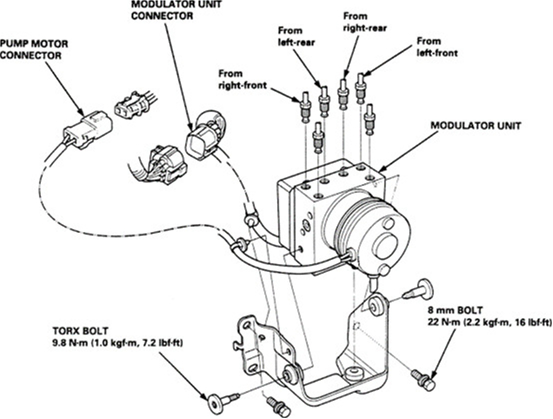
Figure 3: Components of the ABS Pump Assembly. (Source: Internet)
Principles of ABS Pump Operation
- During braking, brake fluid pressure flows from the master cylinder to the ABS pump through the brake fluid lines.
- The ABS pump distributes brake fluid pressure to individual wheels via solenoid valves, which can operate in three positions: open, closed, or partially open.
- Wheel speed sensors monitor the status of each wheel and send signals to the ABS ECU.
- The ABS ECU compares the wheel speed signals with reference values to determine if any wheel is at risk of locking or skidding.
- If a wheel is about to lock or skid, the ABS ECU commands the corresponding solenoid valve to reduce or release brake pressure, allowing the wheel to regain traction and prevent skidding.
- Conversely, if a wheel requires additional brake pressure, the ABS ECU commands the solenoid valve to increase or restore brake pressure, enhancing braking force and reducing stopping time.
- The ABS pump uses an electric motor to restore brake fluid pressure within the system, ensuring sufficient pressure for subsequent braking cycles.
- The ABS control module repeats these steps rapidly (several times per second) based on driving conditions and vehicle speed, creating a pulsating sensation in the brake pedal when the ABS is active.
ABS Pump Maintenance Methods
- Electrical System Inspection
- Check circuits and connections: Ensure all wiring and connections to the ABS pump are free of corrosion or damage.
- Inspect fuses and relays: Confirm that the fuses and relays associated with the ABS system are functioning correctly.
- Wheel Speed Sensor Inspection
- Clean sensors: Dirt can affect the accuracy of wheel speed sensors; ensure they are clean and operational.
- Verify sensor spacing: Ensure sensors are correctly positioned relative to the signal rings for accurate readings.
- Brake Fluid Inspection
- Check and replace brake fluid periodically as recommended by the manufacturer to maintain optimal braking performance.
- ABS Pump and Line Inspection
- Examine the pump and brake fluid lines for any signs of leaks. Address leaks immediately with repairs or replacements.
- Brake System Inspection
- Inspect brake components: Ensure brake discs and pads are within standard limits and replace them as needed.
- Test brake performance: Verify that the ABS system functions effectively and is free of errors.
- Diagnostic Tools
- Error code check: Use diagnostic equipment to identify any fault codes in the ABS system, enabling early detection and resolution of issues.
- Software updates: Ensure the ABS control software is up to date for optimal performance.